As a pediatrician, I understand the concerns parents have about ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) and how diet can influence their child’s behavior and cognitive function. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in brain health. This article aims to educate Indian parents on the connection between ADHD and Omega-3 fats deficiency and provides practical advice on how to mitigate the impact on their children.
What are Omega-3 Fats?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats the body cannot produce on its own, so they must be obtained from the diet. The three main types of Omega-3 fats are:
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): Found in plant oils, such as flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): Found in fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): Found in fatty fish and is crucial for brain development and function.
ADHD and Omega-3 Fats Deficiency
Research suggests that children with ADHD may have lower levels of Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. These deficiencies can affect brain function, leading to symptoms associated with ADHD.
A deficiency in Omega-3 fats can manifest in various ways, often overlapping with ADHD symptoms, including:
A deficiency in Omega-3 fats can manifest in various ways, often overlapping with ADHD symptoms, including:
- Poor Concentration: Difficulty focusing and sustaining attention on tasks.
- Hyperactivity: Increased restlessness, fidgeting, and impulsive behavior.
- Mood Swings: Increased irritability, anxiety, and emotional instability.
- Sleep Disturbances: Trouble falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Dry Skin and Hair: Physical signs of deficiency, such as dry, flaky skin and dull, brittle hair.
What Should Parents Do If Your Child Has ADHD Symptoms?
If your child exhibits symptoms of ADHD and you suspect an Omega-3 fats deficiency, here are steps you can take:
1. Include Omega-3 Rich Foods in the Diet:
- Fatty Fish: Incorporate fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout into meals at least twice a week.
- Plant Sources: Add flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and soybeans to your child’s diet.
- Fortified Foods: Look for Omega-3 fortified foods, such as certain brands of eggs, milk, and yogurt.
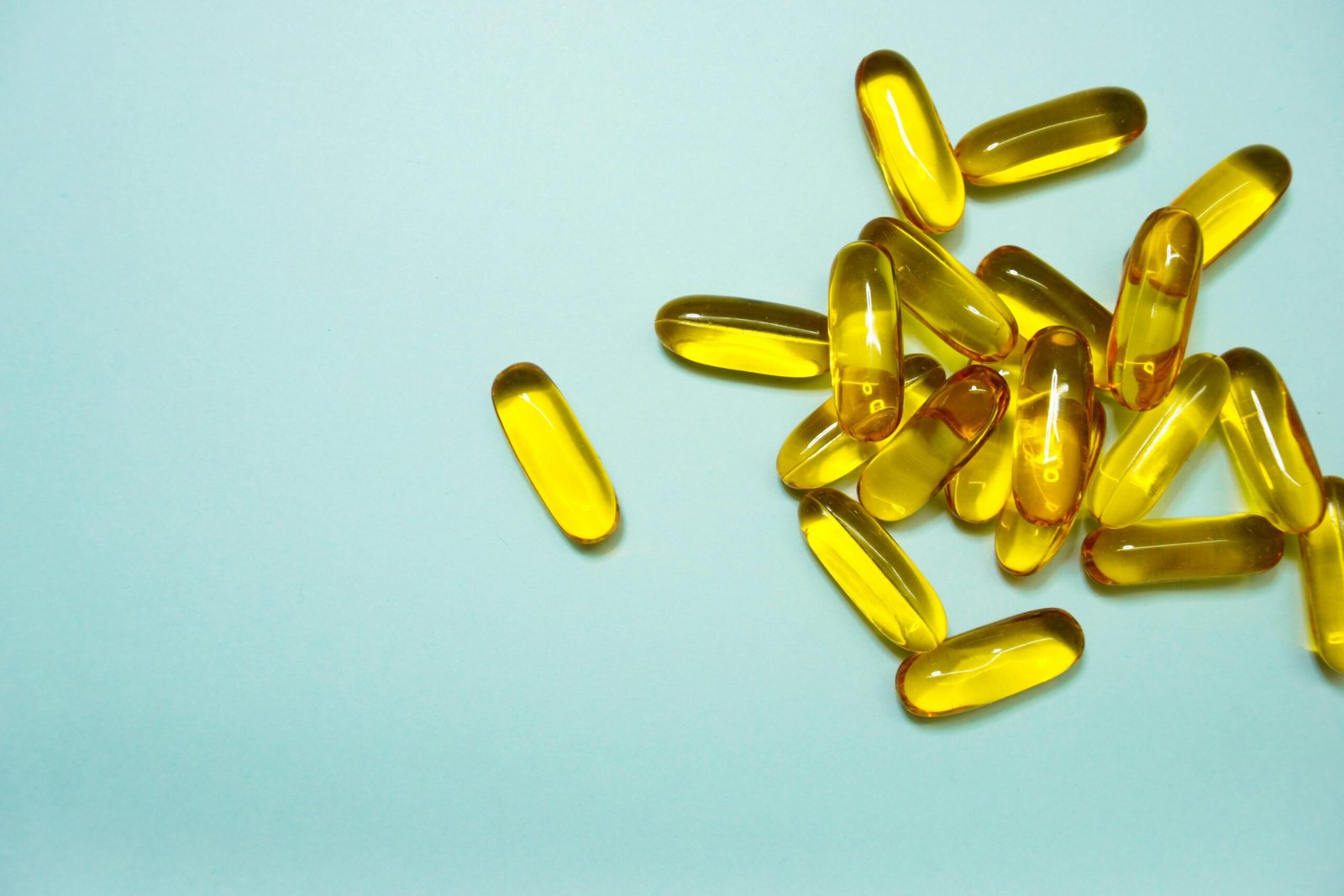
2. Consider Omega-3 Supplements:
- Fish Oil Supplements: High-quality fish oil supplements can help boost Omega-3 intake. Consult with a pediatrician before starting any supplement regimen.
- Algal Oil Supplements: For vegetarian or vegan options, algal oil is a plant-based source of DHA.
3. Maintain a Balanced Diet:
- Ensure your child eats a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, to support overall health and brain function.
4. Monitor and Adjust:
- Keep track of your child’s dietary habits, behavior, and academic performance.
- Be flexible and willing to adjust the diet and supplement strategies as needed.
5. Seek Professional Guidance:
- Consult with a pediatrician or a nutritionist to assess your child’s nutritional needs and create a personalized plan.
- Regular follow-ups can help monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
By addressing Omega-3 fats deficiency, parents can support their child’s brain health and potentially reduce the severity of ADHD symptoms. Early intervention and appropriate dietary management can significantly improve outcomes for children with ADHD.
For personalized advice and treatment options, please consult Dr. Kritika Agarwal, Pediatrician and Adolescent Specialist, at Pinnacle Health Multispeciality Clinic, Hosa Road, Bangalore.