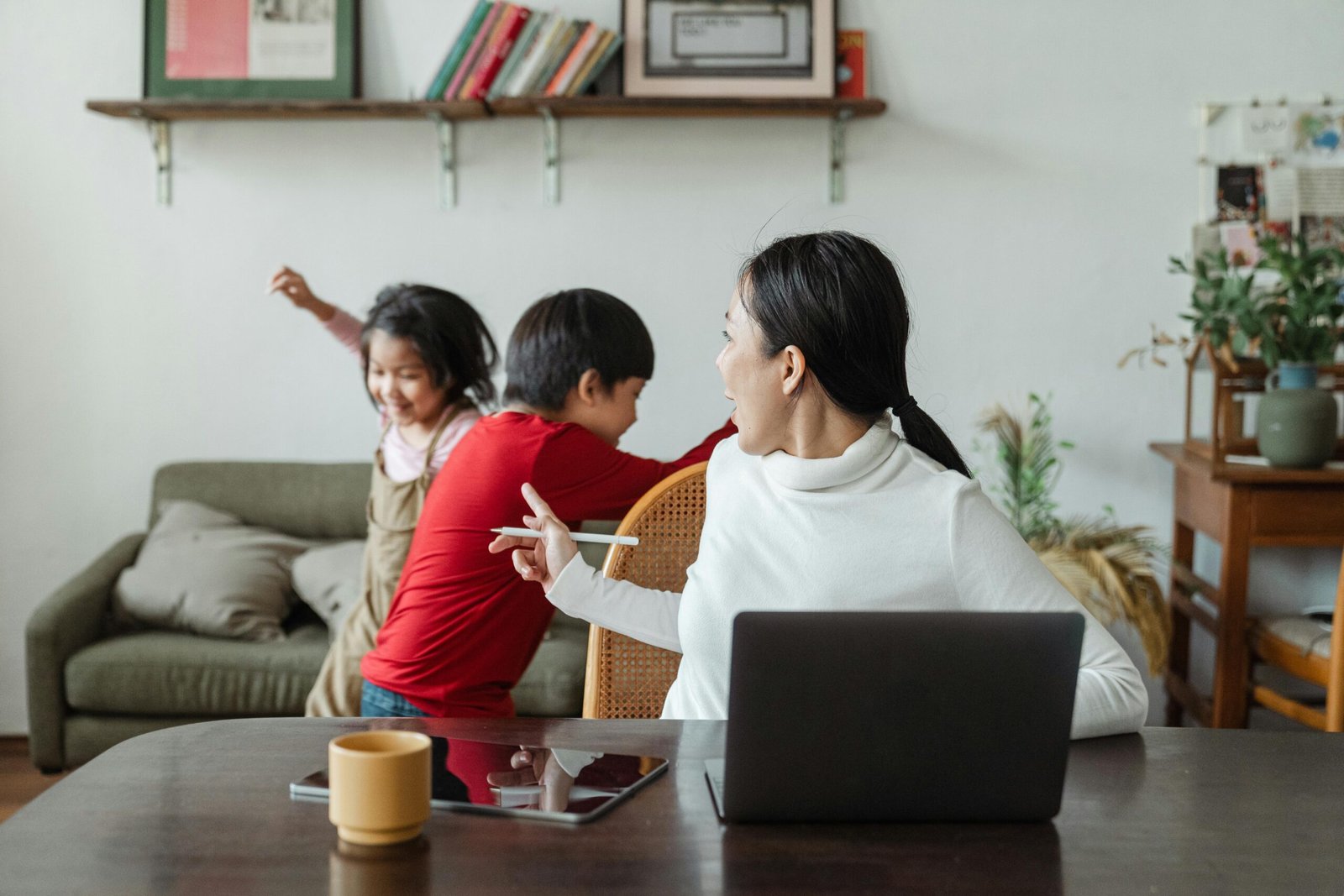
As a pediatrician, I often encounter parents who are concerned about their child’s behavior and wonder if it might be a sign of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Understanding the differences between normal toddler behavior and ADHD is crucial for early intervention and appropriate support. This article aims to educate Indian parents on these distinctions and offer practical advice on managing ADHD if it is diagnosed.
What is ADHD?
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a common neurodevelopmental disorder that affects children. It is characterized by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are more severe, frequent, and persistent than typical childhood behavior.
Who Gets ADHD More?
ADHD affects children worldwide, including in India. It is more commonly diagnosed in boys than girls. The exact cause of ADHD is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors.
Normal Toddler Behavior vs. ADHD Symptoms
Normal Toddler Behavior:
- High Energy Levels: Toddlers are naturally energetic and curious, often running around and exploring their environment.
- Short Attention Spans: It is common for toddlers to shift their attention frequently and be easily distracted.
- Impulsivity: Toddlers may act without thinking, such as grabbing toys or interrupting conversations, as they are still learning self-control.
- Occasional Tantrums: Mood swings and tantrums are a normal part of toddler development.
ADHD Symptoms:
- Inattention: Difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play activities, often seeming not to listen when spoken to directly.
- Hyperactivity: Excessive fidgeting, running or climbing in inappropriate situations, and an inability to stay seated.
- Impulsivity: Blurting out answers, difficulty waiting for their turn, and interrupting others frequently.
- Persistent and Pervasive: These behaviors are consistent across multiple settings (e.g., home, school) and significantly impair the child’s functioning.
Is ADHD Contagious?
ADHD is not contagious. It is a developmental disorder that cannot be transmitted from one person to another. The risk factors for developing ADHD include genetics, prenatal exposures (such as tobacco or alcohol), and early exposure to environmental toxins.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis: Diagnosing ADHD involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, which includes:
- Behavioral Assessments: Gathering detailed information about the child’s behavior from parents, teachers, and caregivers.
- Observation: Direct observation of the child’s behavior in different settings.
- Standardized Rating Scales: Using questionnaires and checklists to assess the severity and frequency of symptoms.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: Ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms, such as learning disabilities or mood disorders.
Treatment: Treatment for ADHD often includes a combination of behavioral therapy, medication, and educational support:
- Behavioral Therapy: Techniques to help children develop social skills, improve self-control, and manage their behavior.
- Medication: Stimulant and non-stimulant medications can help reduce symptoms of hyperactivity and inattention.
- Educational Support: Customized learning plans and accommodations to support the child’s educational needs.
What Parents Can Do to Mitigate Impact?
Create a Structured Environment:
- Establish consistent routines for daily activities such as meals, homework, play, and bedtime.
- Use visual schedules and clear, concise instructions to help your child understand expectations.
Positive Reinforcement:
- Praise and reward positive behavior to encourage desired actions.
- Set achievable goals and celebrate your child’s progress.
Limit Distractions:
- Create a quiet and organized space for your child to focus on tasks.
- Minimize screen time and provide opportunities for physical activity to channel their energy positively.
Healthy Lifestyle:
- Ensure your child gets regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support brain health.
Seek Professional Support:
- Collaborate with teachers, counselors, and healthcare providers to create a comprehensive support system for your child.
- Attend parent training programs to learn effective strategies for managing ADHD.
By recognizing the differences between normal toddler behavior and ADHD, parents can take proactive steps to support their child’s development and well-being. Early intervention and a supportive environment can significantly improve outcomes for children with ADHD.
For personalized advice and treatment options, please consult Dr. Kritika Agarwal, Pediatrician and Adolescent Specialist, at Pinnacle Health Multispeciality Clinic, Hosa Road, Bangalore.